
Joe
November 27, 2025
Authenticating to Azure SQL Using C# (.NET 8) + DefaultAzureCredential + User-Assigned Identity
Learn how to securely connect a .NET 8 Azure Function to Azure SQL using DefaultAzureCredential and a User Assigned Managed Identity. In this guide, we walk through creating a clean architecture setup, implementing an authentication-aware connection factory, and configuring your Azure Function App to authenticate without storing credentials. Perfect for developers looking to modernize their SQL access with fully managed, token-based security.
🔐 Authenticating to Azure SQL Using C# (.NET 8) + DefaultAzureCredential + User-Assigned Identity
Hi all! 👋
In this post, I’ll walk you through how to authenticate to an Azure SQL Database in C# (.NET 8) using:
DefaultAzureCredential()🚀- A User Assigned Managed Identity (UMID) 🆔
- A clean architecture function app running in Visual Studio 2022 ⚙️
This setup is secure, production-ready, and avoids storing any SQL credentials.
📁 Function App Solution Structure
Here's what my function app looks like in Visual Studio 2022:
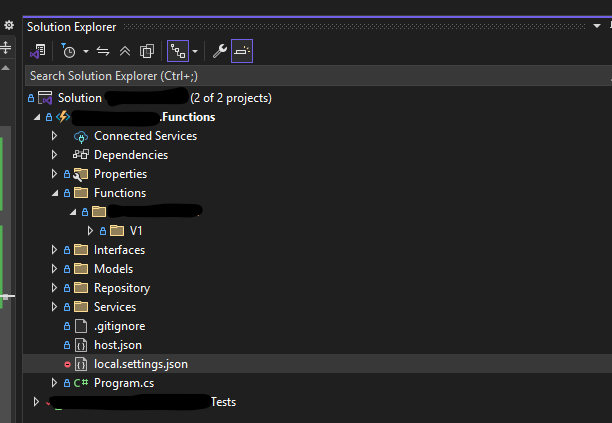
I’ve followed a Clean Architecture approach and also enabled function versioning (I'll write a separate post about versioning soon 😉).
🧩 Interfaces
To begin, I created an interface called IDbConnectionFactory.cs:
public interface IDbConnectionFactory { /// <summary> /// Creates and opens an authenticated database connection. /// Uses managed identity for secure authentication to Azure SQL databases. /// </summary> Task<IDbConnection> CreateConnectionAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default); }
⚙️ Implementation of the Database Connection Factory
Next, here's the class that implements the interface. This class handles:
- Getting an Azure AD token 🔑
- Setting it as the SQL access token
- Handling timeouts ⏳
- Handling SQL exceptions with meaningful messages ⚠️
public async Task<IDbConnection> CreateConnectionAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default) { var connection = new SqlConnection(_connectionString); try { // Only add token when Authentication isn't already defined if (!_connectionString.Contains("Authentication=", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase)) { var tokenRequestContext = new TokenRequestContext(new[] { "https://database.windows.net/.default" }); var accessToken = await _credential.GetTokenAsync(tokenRequestContext, cancellationToken); connection.AccessToken = accessToken.Token; } using var timeoutCts = CancellationTokenSource.CreateLinkedTokenSource(cancellationToken); timeoutCts.CancelAfter(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(30)); await connection.OpenAsync(timeoutCts.Token); if (connection.State != ConnectionState.Open) { throw new InvalidOperationException($"Connection failed to open. State: {connection.State}"); } return connection; } catch (OperationCanceledException ex) when (cancellationToken.IsCancellationRequested) { connection.Dispose(); throw new TimeoutException("Connection opening was cancelled by caller.", ex); } catch (OperationCanceledException ex) { connection.Dispose(); throw new TimeoutException("Timed out while opening SQL connection.", ex); } catch (SqlException sqlEx) { connection.Dispose(); var errorMessage = sqlEx.Number switch { 2 => "SQL Server not reachable. Check server name/network.", 18456 => "Authentication failed. Check UAMI permissions.", 4060 => "Database not found. Check DB name.", _ => $"SQL error occurred (Error Number: {sqlEx.Number})" }; throw new InvalidOperationException(errorMessage, sqlEx); } catch (Exception ex) { connection.Dispose(); throw new InvalidOperationException("Unexpected error opening SQL connection.", ex); } }
⚙️ local.settings.json
My local settings file contains a simple connection string I've hidden everything else:
"ConnectionString": "Server=tcp:SERVER_NAME.database.windows.net,1433;Database=DATABASE_NAME;TrustServerCertificate=False;Connection Timeout=30;"
🧠 Program.cs
This is where the configuration and dependency injection happen:
// Load config var config = builder.Configuration; config.SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()) .AddJsonFile("local.settings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true) .AddEnvironmentVariables(); builder.ConfigureFunctionsWebApplication(); var connectionString = config["ConnectionString"] ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Database connection string is not configured."); builder.Services .AddApplicationInsightsTelemetryWorkerService() .ConfigureFunctionsApplicationInsights() .AddApplication() .AddDatabase(connectionString); builder.Build().Run();
💉 Dependency Injection — DIServices
public static IServiceCollection AddDatabase(this IServiceCollection services, string connectionString) { services.AddSingleton<IDbConnectionFactory>(new MssqlConnectionFactory(connectionString)); return services; }
☁️ Azure Configuration (Important Part!)
To make this work in Azure Functions, you must configure your App Settings correctly.
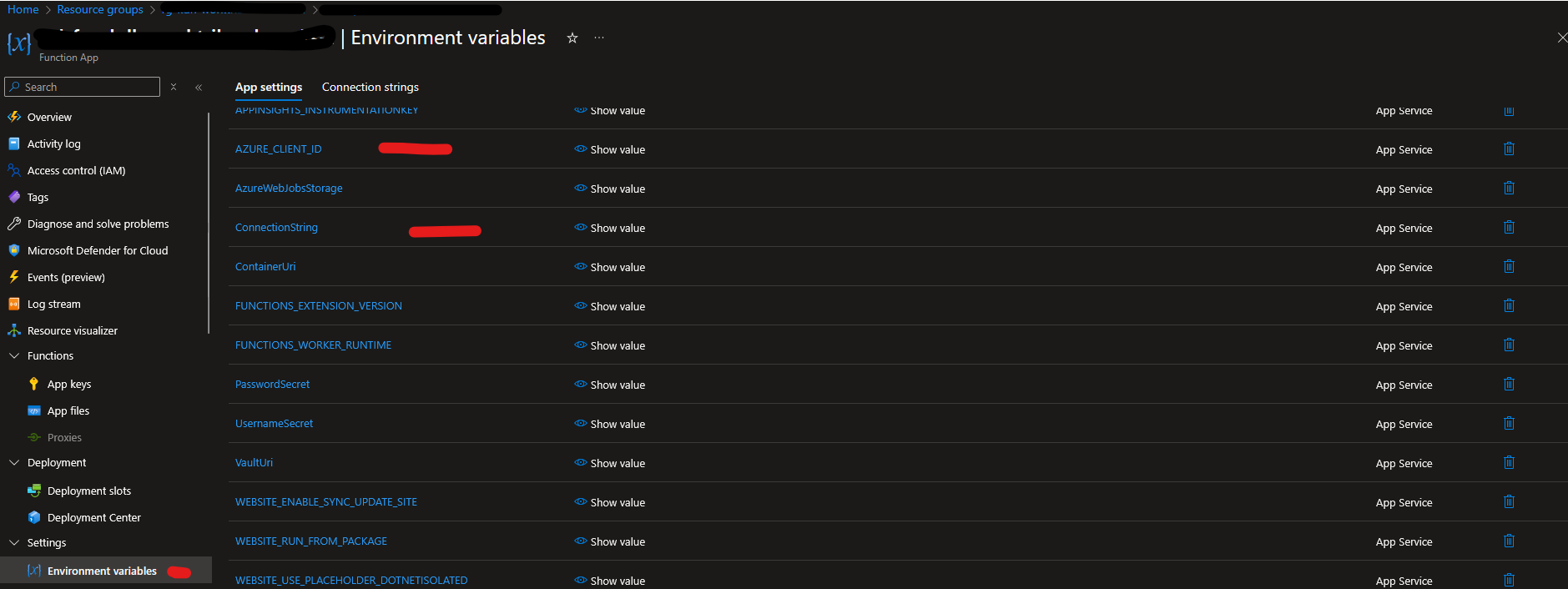
🔴 Key setting: AZURE_CLIENT_ID
This must contain the Client ID of your User Assigned Managed Identity. This allows DefaultAzureCredential() to know which identity to use.
📌 You'll find it here:
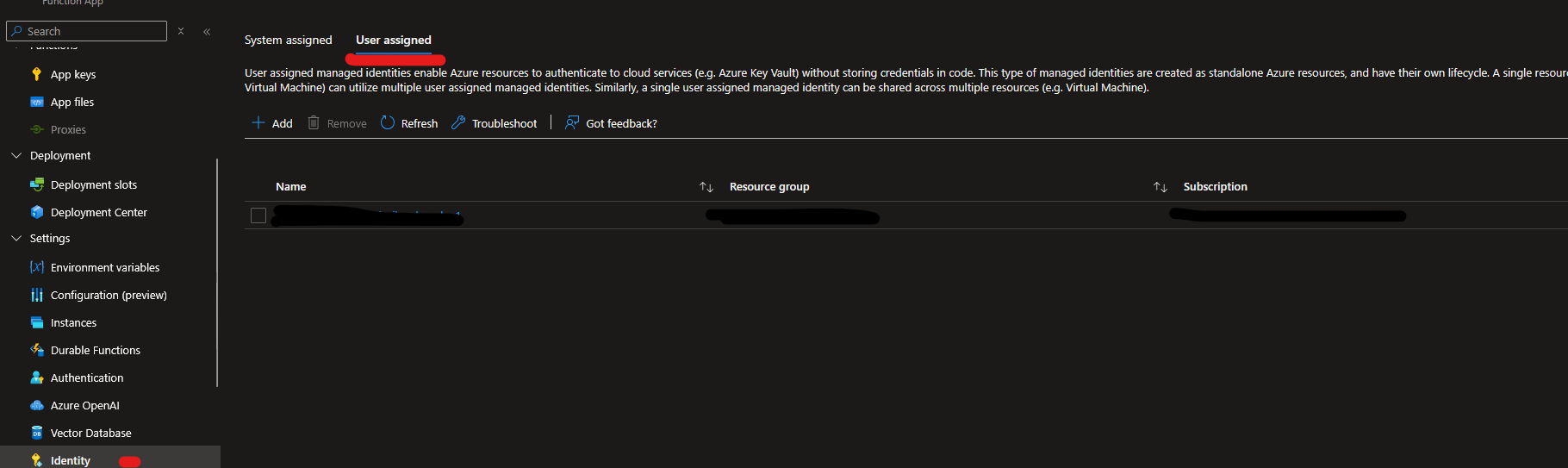
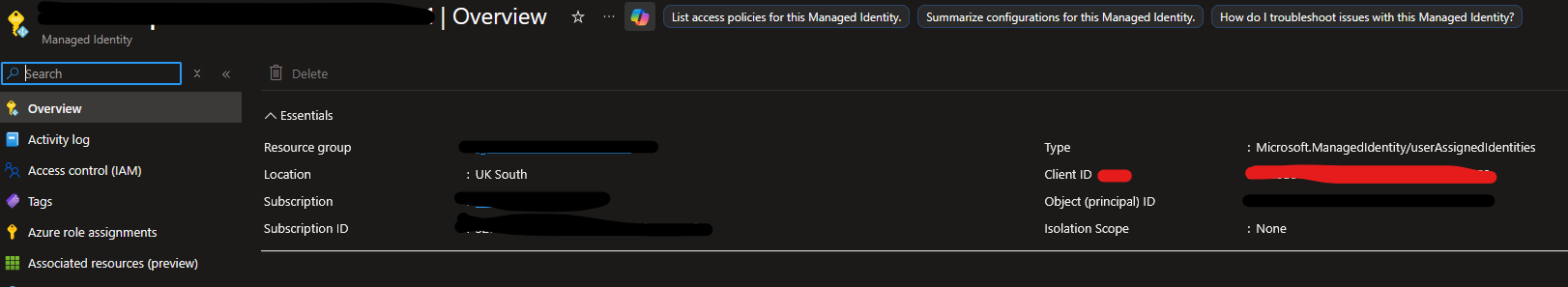
🎉 Final Step — Deploy & Test
Once everything is deployed:
- The function app uses the User Assigned Managed Identity to request a token
- Azure SQL validates the identity
- Token-based authentication succeeds 🔐
- Your connection opens — no username or password required 🎯
If everything is configured properly, you should now be able to connect to Azure SQL securely.
📬 Need Help?
If you run into issues, feel free to message me on LinkedIn — always happy to help! 😊